The A to Z of the Equifax Credit Report
We began the discussion about how you can read your credit report in Canada. In that blog, we also discussed the various items found on the credit report from Transunion. Therefore, this blog will take hints from the previous one and expand your knowledge of reading credit reports. Specifically, we will dwell on the Equifax credit report and the elements found therein.
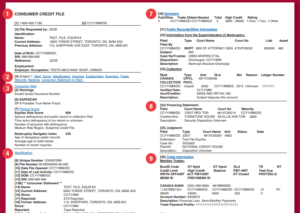
Equifax Credit Report Sample
Brief Overview of the sections of Equifax credit report
- Phone number submitted to Equifax
- The date you requested for file
- Inquirer’s data
1. Identifying information
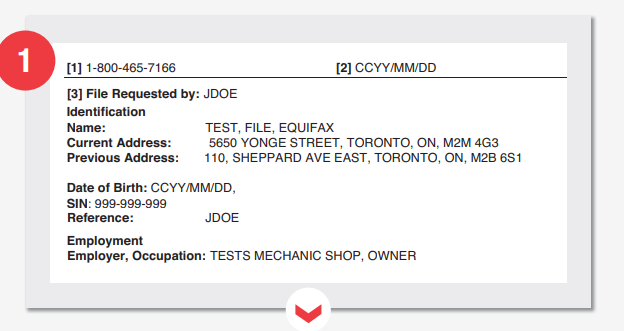
This Equifax report section has your name, address, date of birth, and social security number. However, it is worth mentioning that the companies don’t use these identifying information to calculate your credit score. Also included in the report are your current and previous address and your occupation and employer. It is also worth noting that each report refers to whoever requested it as indicated in the attached sample. For example, in the case shown in the image above, JDOE requested a person test’s credit report. The inquirer’s data referred to in 3 above is the information provided, requesting the credit file. For the example case, only a name was provided.
Benefits
- Helps with verifying client’s data
- Improves quality and precision
- The faster file search process
- Assists in fraud prevention and detection
- Sections for the displayed files
The subject 1 part of the report communicates which parts have been filled with data and shown to the user. This is important as it highlights what data the user can get from the file. Therefore, an experienced user may know what is missing from the first look.
- Alerts consumer against incorrect data
Essentially, this section clarifies the validity of user information. It is generally comparing the records on file and what you supply to the system when requesting the report. So, suppose you miss a number or hit the wrong button when entering the social insurance number. In that case, an error will show indicating that the social insurance number has discrepancies.
- Warns client against fraud
In case you haven’t heard about it yet, SafeScan is an automated fraud screening tool that warns users of fraudulent individuals, businesses, and transactions. Note that the SafeScan section is only available to its subscribers. The credit report will have an SF-9 code on this section if someone is attempting to apply for credit with the wrong details.
- Indicates information that created a negative effect on the report
This section indicates the risk score Equifax has assigned an individual. Below the credit score, you will find the various reasons for the current score. Put it simply, this is a kind of justification for the score, and it briefs the holder of the report of your financial activity. Again, this feature is only made available to entities that subscribe to risk scores.
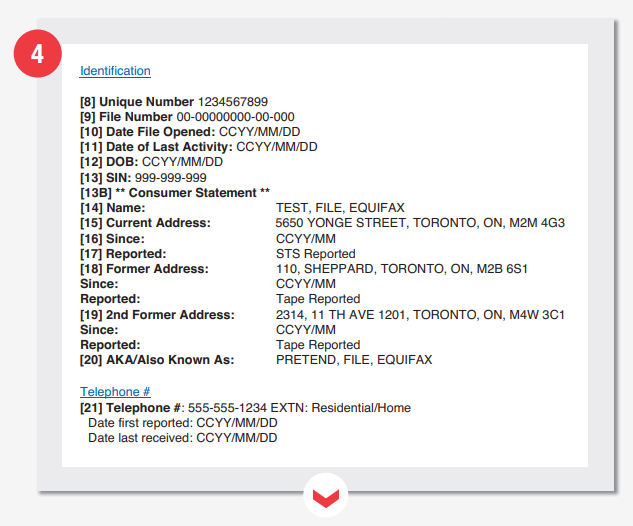
Identification Section
- Consumers File Identification Number
- The file number for official use
- Date of file creation
- The date the file was last updated
- Consumer’s date of birth
- Insurance number & Consumer statement
- Name of Subject
- Current Address
- The initial report of address –
- Mode of information collation
- Subject’s previous address
- Any other address
- Information is under the provided names
- Consumer’s telephone, date of the first report, and last receipt
As you can see from the items listed above, this section is quite elaborate and easy to understand. However, the unique number and the File number are sometimes confused. The former is a unique identifier that a user can use about their file, while the latter is a number only used by Equifax.
The information collation mode, the “Reported” clause in the image above, shows the report holders how data reached Equifax. DAT reported means that the information was fed into the system through a direct access terminal. Tape reported that an electronic reporting customer reported that data was reported while STS reported that a direct link customer reported your credit activity. All other info shown in this section can be interpreted as it appears.
Benefits
- Assists in providing accurate consumers’ information
- Up to three addresses, current and former
- Most creditors may report the age instead of birth date to protect client’s privacy
- Insurance number also helps in client’s verification
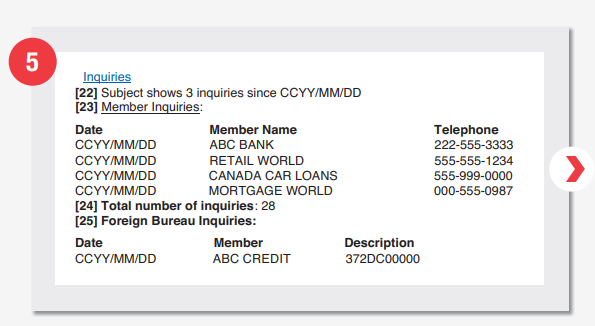
Inquiry Section
- Indicates inquiries launched within the past three months
This item will only have data if a user’s account has received at least three inquiries in 90 days.
- Enquirer’s information for past 36 months’ inquiry
The credit report does not leave some stones unturned because besides showing the warning in clause 22 above. It also goes ahead to list the entities that inquired. Entities that made inquiries in the last 12 months will be shown alongside their phone numbers. However, those who inquired before then will appear as a list of names only. All inquiries listed in this clause are within 36 months from the date the report is obtained.
- No. of inquiries since file creation
- Details of Foreign Enquirers
If any foreign bodies are inquiring about your credit history, they will be listed under this clause. Unlike with local inquiries, only a name, date of the activity, and a short description are provided.
Benefits of Inquiry Information
Equifax offers two inquiry types, such as soft and hard.
Soft Inquiry
This results when
- Companies extend your pre-approved credit offers
- Check your credit reports
- Your current creditor or lender conducts periodic reviews
Soft inquiries have close to zero effect on your credit score but will help you monitor your account and eliminate theft and errors.
Hard Inquiry
A hard inquire occurs when
- You apply for credit from individuals or financial bodies, and
- Companies or individuals review your Equifax credit report.
Unlike soft inquiries, hard inquiries will remain on your credit report for about two years. It impacts your credit score negatively, but the impact wanes overtime.
Employment Section
- Details of Current Employer
The current employer clause indicates the most recent economic engagement of the subject. However, if the subject is not employed but owns a town franchise, it will be termed as the employer. Therefore, clause 27 below will refer to the person as the owner of the said franchise. See the example in the image above.
- Since, Left date, Position, Salary.
Clause 27 aims to show the subject’s position at their recent economic engagement and the duration they served. Even though this information may not directly impact your credit score, different lenders may interpret it to gain useful insight. If the person is the venture owner, the salary bullet will indicate “Owner” instead of showing a figure.
- Previous employer information – Position, Salary, start date, and Left date\
Like in section 27 above, the former employer details are indicated here. Clause 29 hence follows the procedure for 27 and 28.
- Second employer information – Position, Salary, start date, and Left date
Benefits
- Includes up to three employers; current and two previous
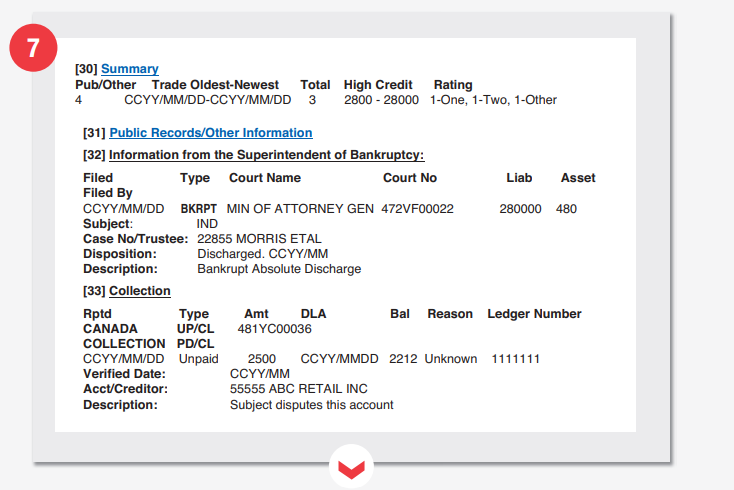
Summary Section
- Number of public records information obtained.
This section shows various pieces of information that is publicly available or which have been reported to Equifax. In this section, you will find the total number of transactions and the range of credit advanced to the individual in question. The trades are recorded from the oldest to the newest, and each comes with a credit rating for the time it was executed.
- Public records information
If the said user has been involved in a public court case, the information of the proceeding of such a case will be listed under this clause. Therefore, there may be no data if the user has not been to court.
- Bankruptcy info
If a person has been declared bankrupt, then it shows they are unable to repay their debts. This information is obtained from the superintendent of bankruptcy and includes the following details:
- The date when bankruptcy was filed
- Type of action (IND- individual and BUS for business)
- Name and code of the court where the case was filed
- The case number
- Disposition of the case
- Description of the bankruptcy
33 Details of third party creditor
If, in any case, the subject has debts which the original lender has since forwarded to debt collection agencies, the relating information will be listed under this clause. Therefore, it will be easy for anyone holding a credit report to discern if the borrower has ever had a bad debt before. The details listed on the records include the member number of the collection agency, the name, date of reporting, the status of the debt indicated as UP CL to mean the unpaid collection, or PD CL to mean debt paid through collection and original debt amount among other fine details.
Benefits
- Bankruptcies
Your Equifax credit report has bankruptcy records such as type and filling date.
- Collections accounts
This contains account information that has been sent to collection agencies. This section contains your credit accounts and other accounts with banks, doctors, companies, and mobile phone operators.
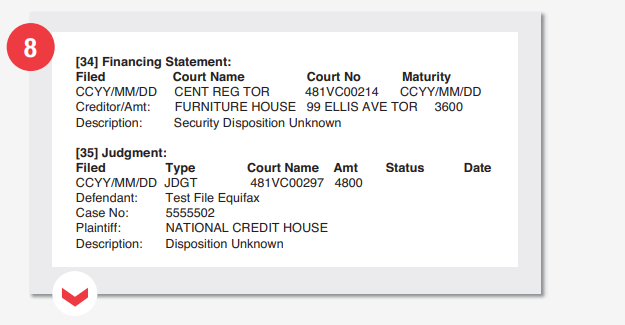
Finance Statement
34 Credit financing statement
Outside the Quebec province of Canada, people can obtain secured loans from lending institutions. However, each such loan must be registered with the provincial government. Additionally, a registered loan, a chattel mortgage, a lien, and any other lending form to which collateral is attached must be registered. Here is a breakdown of the details of a credit financing that appear on the report.
- Date reported
- Name of the reporting agency
- Member number (reporting agency)
- Loan maturity date
- Identifying information of the creditor
- Loan amount and status
- Court orders and related judgments
This clause takes care of judgments made in a court of law against any particular debt payment.
Trade Information
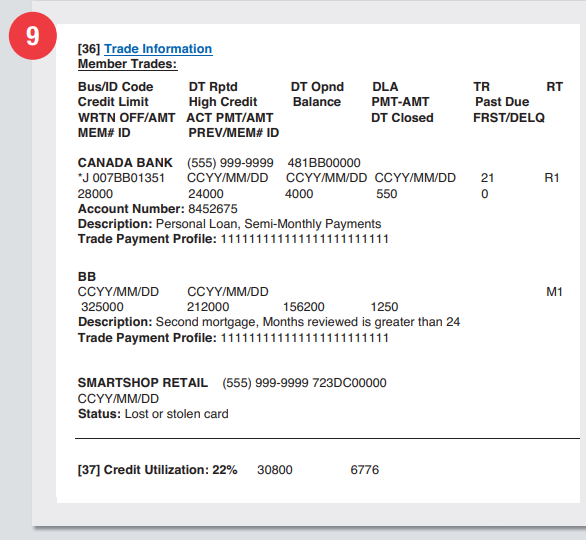
DT RPTD – Date of the report to Equifax
DT OPND – Date account was created
DLA – Last activity date
TR – Reported account upgrade
RT – Mode of repayment and account type
Banking Information Section
Credit account information
Your creditors and lenders will forward your credit information to Equifax. These include account types, dates accounts were opened, account balances, your loan limit, and payment history. Closed accounts that are no longer valid for your report will not be reported to Equifax.
- Consumer Account Statement and Declaration
Images culled from https://assets.equifax.com/assets/canada/english/consumer_credit_report_user_guide.pdf.
Common errors on your credit report
Once your credit report arrives, check for possible mistakes in your name, address, and birth date. Also, check against errors in your loan and credit card accounts, especially on repayment dates. Ensure there is no negative information exceeded its allowed time, which could mar your chances of securing credit. Another common error to ward against is listing accounts you never opened and false identity.
Details not included in an Equifax Credit Report
- Bankruptcies over 10 years’ old
- Savings account information
- Debts or collection items over seven years
- Gender, religion, ethnicity or political affiliation
- Criminal records
- Medical history
- Motor vehicle records
- Items bought by credit card.
How to fix credit report errors?
Below are the few things you must follow to clear all errors from your report.
- Get enough evidence, including account statements and receipts, to back your claims.
- Contact your bureau and fill a copy of the error correction form. The agency will investigate your information with the lender before effecting changes.
- Draw your creditor’s attention to the errors and inform them to verify your details with the agencies.
- You can speed up the correction process when you offer to speak with a third-party complaint resolution body.
- Submit a statement that explains your position and level of satisfaction with the handling of your case.
- If you’re still not satisfied with the credit bureau, you can complain to your provincial consumer office agency. You can locate your office of consumer affairs here.
Difference between a free and paid credit report
Both free and paid credit reports have different content; again, you have more benefits with a paid option.
For example, a paid report contains a value compared to the credit bureau’s description to determine your creditworthiness. Besides, a paid credit report is well-detailed, letting you know if your credit status will improve or get worse. This information is more reliable since it’s a product of analysis; hence, you can make the right decision.
Sometimes you’ll notice only a slight difference between free and paid credit reports. But we can’t say the same for your credit score because of the model used. Of course, most reports won’t contain your credit score because companies use different models in their calculations.
Depending on their standard model, lenders usually pay some money to get your credit score. So, if you apply for a loan from different lenders, each could get a different credit score. That said, there are no significant differences between the two reports except when requested by different lenders.
Since companies want to evaluate your risk profile, they need every relevant detail and wouldn’t mind paying. Meanwhile, what you get for free will slightly differ from what companies get when they pay.
Credit report personal information
Each credit report agency has its way of collating data. You’ll likely find the following financial/personal information in your credit report.
Financial information
- Comments, including users’ affirmation, fraud/identification verification alerts
- Insufficient funds remittance, or substandard checks
- Bills sent to assembling agencies
- Investigations from issuers and others who demanded your credit report over the past three years
- Liquidation or a court resolution in opposition to you relating to credit
- Recorded things like charge on a vehicle that permits the lender to collect it back if you’ve not paid
- Used loan, including credit cards, shop or selling cards
- Savings and current accounts that one closes as a result of money debt or fraudulent act
Other genuine information in your credit report about credit cards and overdraft
- The date of account opening
- How much you’re owing
- Timely payment
- Whether you skipped any payments
- Bill transferred to a collating agency.
- If you passed your credit restriction
Personal information
- Full names
- Date of birth
- Current and previous addresses
- Current and former mobile numbers
- SIN (social insurance number)
- Driver’s license information
- Passport number if any
- Current and prior employers if any
How long will negative information stay on your credit report?
The Canadian Financial Consumer Agency states that negative information can only stay in your report for about 6 to 7 years.
Why your credit information matter?
Lenders use your credit score to know how well you can repay a loan. Your credit score determines the interest attached to the loan. If you have a good score, you stand a good chance of getting a lower interest rate. You will pay a fee anytime you order for an online credit report. Meanwhile, Transunion offers free online credit report service once a month.
What are the benefits of a credit monitoring service?
Canada’s top credit bureaus and other financial institutions offer credit monitoring services. The purpose of these services is to notify you once there’s an action on your credit file. You can use these periodic updates to check fraud and data breach. They help you to take immediate action whenever someone tries to apply for credit in your name. But these services aren’t free.
How often do they update credit reports?
Creditors send data to credit bureaus every month. But, there’re no specific day agencies update the information. However, credit bureaus often receives information from a user each first day of the month. They also get another update on the 15th.
So, credit reports may differ depending on the time creditors forward payment records.
How long does information remain on credit reports?
- Real inquiries that credit grantors make remains for a minimum of three years.
- Credit history and bank information for six years from the date of the last undertaking.
- Bankruptcies can stay for six years after the time of the 1st report.
- Collections take effect for six years since the previous period it occurred.
- Secured loans span for six years after the last activity.
What if there’re mistakes on credit reports?
Even if you don’t need a new loan, reviewing your credit report from each bureau yearly is ideal. That will enable you to identify the wrong information.
Only the data provider and the credit collection department can correct mistakes. Of course, this is according to the Federal Credit Reporting Act. So, you’ll need to initiate a dispute if such cases arise. You will also need to tender your argument through writing. But, this should not be later than 30 days.
How to improve your credit history?
To acquire those savings, take a look at the following tips:
- Access credit reports yearly, arguing any mistakes that might damage your report.
- Apply for loans when you need it, keeping minimal credit queries.
- Pay bills regularly without any delay.
- Keep the appropriate sum of unused credit.
Wrapping up on credit reports
Do you wish to get your credit report? We believe you have everything needed to get it started. Bear in mind that lenders use credit reports to access a consumer’s ability to repay a debt. Credit reports show your payment history and how frequently you were able to make it. People that have higher credit scores always get low-interest rates. They also receive approved reward credit cards.
If your credit report is full of mistakes and problems, you might have a low credit score. Thus, they might be restrictions when you want to purchase specific items or higher interest rates. Try and be more watchful with your credit report when you intend to apply for a loan.
Frequently asked questions
Q: Can I get a free copy of my Equifax credit report?
Yes. Equifax will give you a free copy of your report of you contact them through either on their phone line: (800) 465-7166. You can also fill a request form that is available here if you would like to receive the report in your email or fax. After filling the form you must send it through fax or office address.
You will also be assisted if you visit one of their office locations in person.
Q: How can I reduce that chances of falling victim of identity theft?
There are various ways to avoid falling victim to fraudsters. Here are some helpful pointers:
- Take good care of your credit cards, chequebooks and report if any suspicious thing happens.
- Always read your credit card statements.
- Find more details here.
Q: How is information on my credit report used?
Members of the Equifax community may view your credit report and use the info therein if they have a reason to or have your consent to view your info. People may also view your credit report for purposes within the law. Information on the credit report is basically used to make the best decisions that may affect you. Equifax also uses your report to improve their services and solutions.
Q: What are the factors that negatively impact a credit score?
There are various factors that could affect your credit score. The names or references made to these may differ between institutions but here are the common terms you will likely hear about.
- You have too many unsettled accounts
- Quick borrowing
- High amounts on accounts with credit
- Delinquency
Find more details here.
Source links
https://loanscanada.ca/credit/how-to-read-a-credit-report/
https://loanscanada.ca/services/loans/
https://www.nomoredebts.org/blog/how-to-read-your-credit-report
https://www.debtcanada.ca/library/credit-rating-101
https://www.is650agoodcreditscore.com/fico-credit-score-chart/